The Technological Revolution in Traceability, Logistics and Operational Intelligence
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology is a cutting-edge tool that allows assets to be identified, tracked and managed automatically and without physical contact. Using radio waves, RFID transforms the way businesses operate, offering total visibility of their processes in real time, increased efficiency and reduced human error.
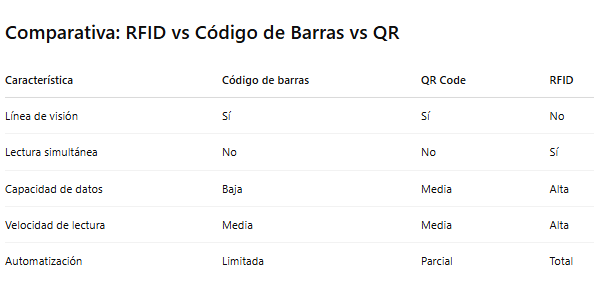
Unlike traditional barcodes or QR codes, RFID requires no line of sight and can read multiple objects at the same time, even while in motion. This capability has made it a mainstay for industries that demand accuracy, speed and traceability.
How does RFID technology work?
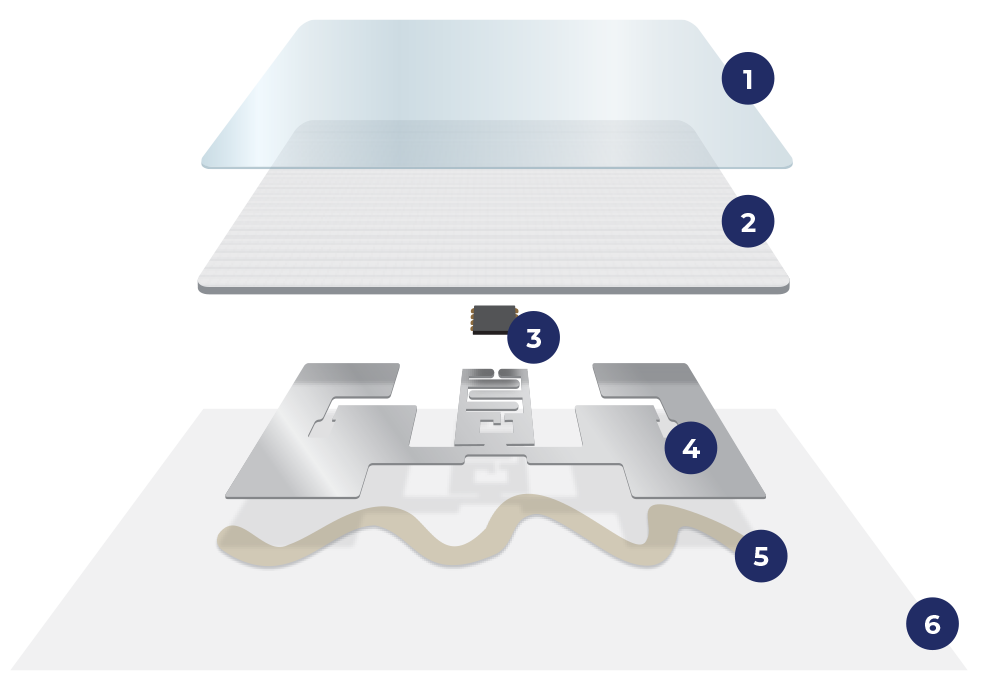
An RFID system is made up of three essential elements:
-
RFID tag: contains a microchip with unique information about the object or product.
-
RFID antenna: emits and receives radio signals between the reader and the tag.
-
RFID reader: interprets the data transmitted by the tag and sends it to the management software for analysis or automation.
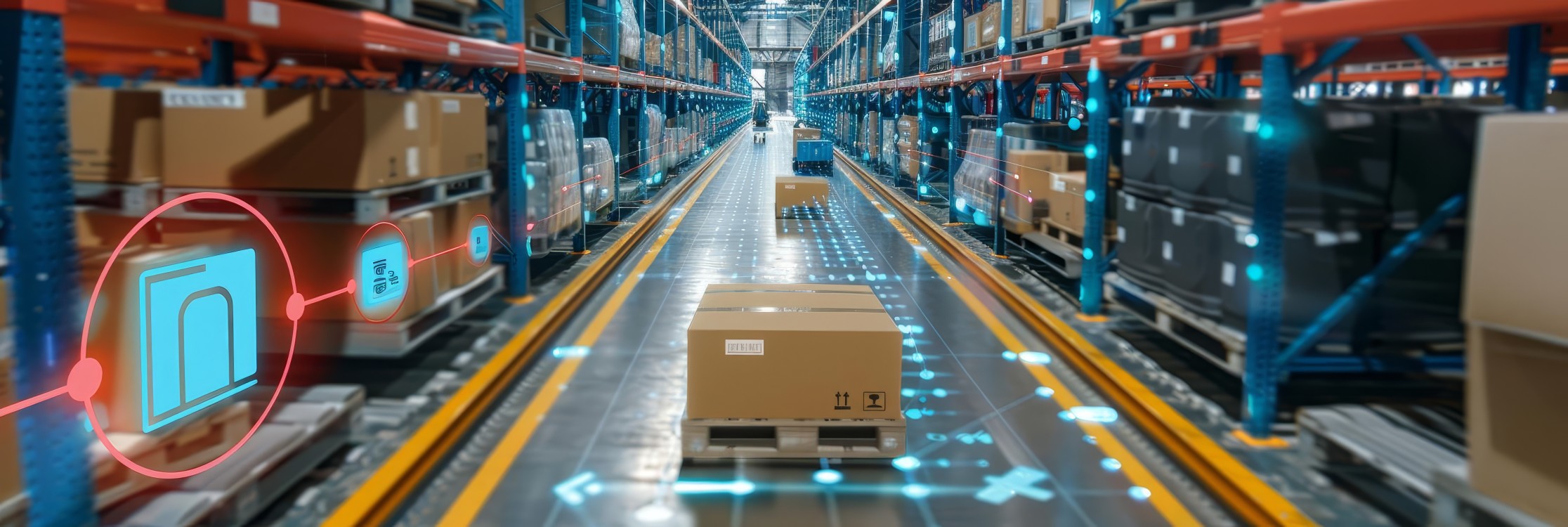

This system allows information to be captured from multiple tags at the same time, with a range that can go from a few centimetres to more than 10 metres, depending on the frequency used and the type of tag.
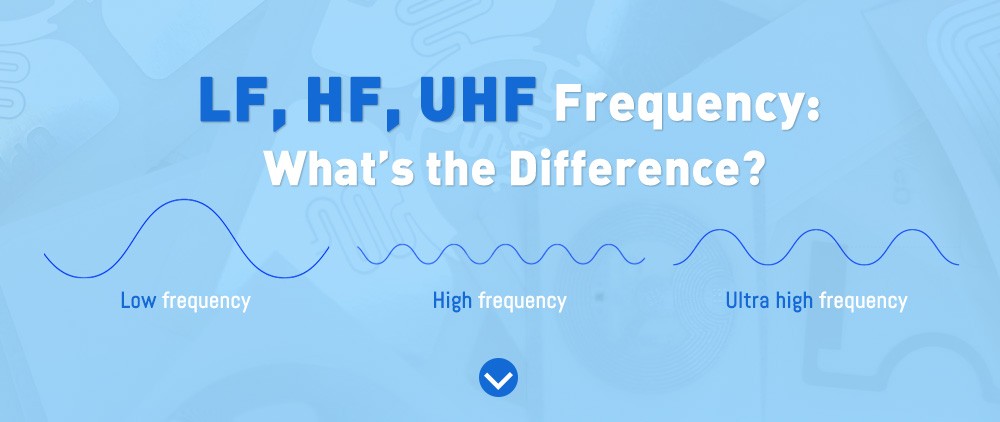
RFID types by frequency
RFID technology is classified according to the frequency at which it operates:
-
LF (Low Frequency – 125 kHz): short read distance, ideal for access control and animal traceability.
-
HF (High Frequency – 13.56 MHz): used in transport cards and contactless payments.
-
UHF (Ultra High Frequency – 860-960 MHz): longer read range, perfect for logistics, retail, industry and healthcare.
RFID tags: passive, active and semi-active
-
Passive tags: they do not have their own battery and are activated by the reader’s signal. They are the cheapest and most common.
-
Active tags: incorporate a battery and can transmit constantly. They are used for tracking high-value or moving assets.
-
Semi-active tags: have a battery but require external activation. They balance cost and performance.
Benefits of RFID technology
RFID is not just an identification tool. It is a strategic enabler of digital transformation. Its benefits include:
-
Simultaneous reading of multiple objects
-
Real-time data for agile decision making
-
Reduction of human error
-
Process automation
-
Increased operational efficiency
-
Increased security and traceability
-
Integration with enterprise software (ERP, WMS, CRM)
RFID applications by sector
Logistics and supply chain
-
Automated inventory
-
Real-time product traceability
-
Error or theft detection
-
Smart warehouse management
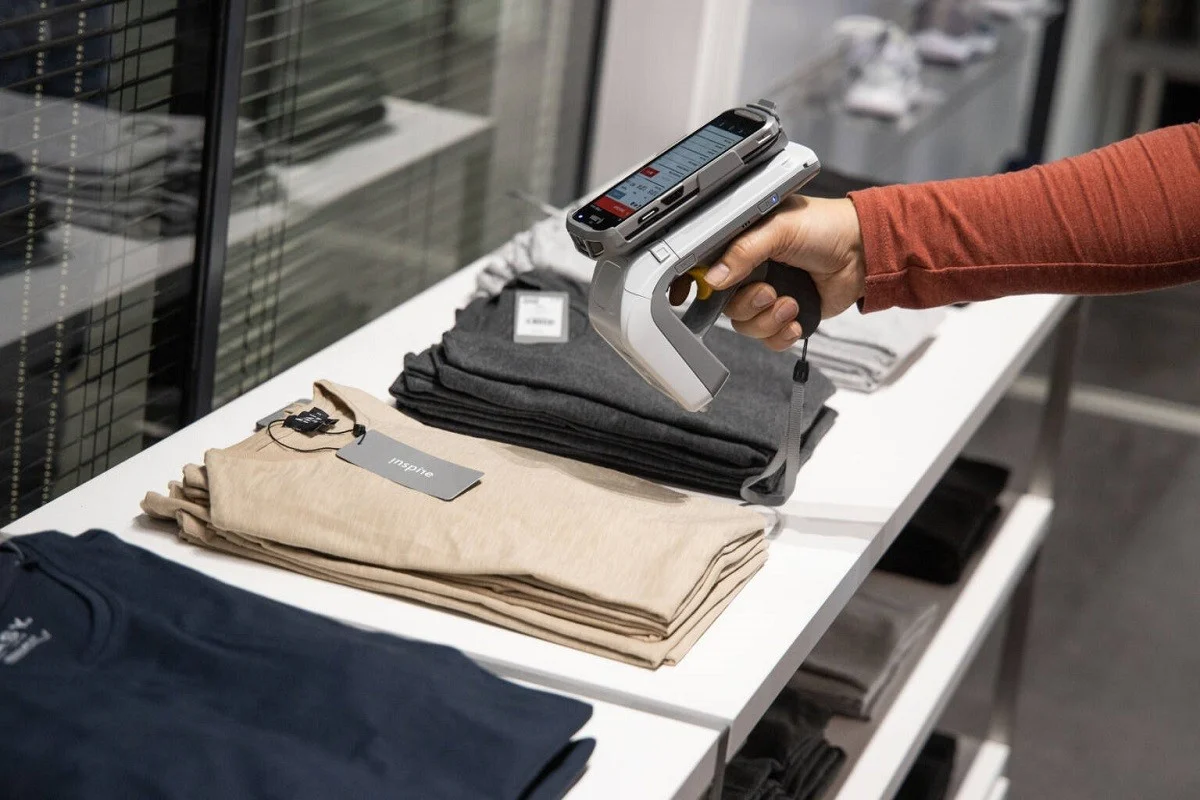
Retail and fashion
-
Real-time in-store and backroom inventories
-
Improved customer experience
-
Reduction of shrinkage
-
Frictionless omni-channel

Healthcare
-
Secure patient identification
-
Medical asset management
-
Medication and clinical documentation control
-
Traceability of blood and samples
Food and cold chain
-
Real-time temperature control
-
Batch and expiry date recording
-
Regulatory compliance and food safety
-
Product traceability in case of recall
Industry and manufacturing
-
Traceability of production processes
-
Tool and component control
-
Improved quality management
-
Predictive maintenance
Security, privacy and compliance
A common concern about RFID is data security. Today, advanced RFID systems offer:
-
Data encryption
-
Reader authentication
-
Access control
-
Protection against tag duplication
In addition, there are international standards such as ISO 18000, EPCglobal Gen2 or NFC Forum that regulate their operation and global compatibility.
The future of RFID: integration with IoT, Big Data and AI
RFID is not an isolated technology. Its power is multiplied by integrating with Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence, Big Data and blockchain solutions.
For example:
-
RFID devices connected to sensors for environmental monitoring.
-
Predictive maintenance processes using advanced analytics
-
Full automation of warehouses and cashierless shops
-
Product authenticity verification using blockchain
Trace-ID: Your strategic RFID partner
At Trace-ID we are expert RFID tag manufacturers. We have been creating solutions adapted to the real needs of each sector for more than 20 years.
We offer:
-
Passive, active and customised RFID tags
-
RFID hardware (readers, antennas, printers)
-
Consulting and integration of RFID systems
-
Specialised technical support
Whether you work in retail, food, healthcare, industry or logistics, we help you design and implement RFID Technology in your company, with our customised RFID tags for each requirement making your RFID system more efficient and smarter.
Contact us today and transform your value chain with RFID.
RFID Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Does RFID replace barcodes?
In many cases, yes. RFID offers more speed, automation and accuracy.
How much does it cost to implement RFID?
It depends on the project, but the ROI is usually high due to operational savings.
Is it difficult to integrate RFID into an existing system?
No. At Trace-ID we help you with progressive and scalable integration.

Contact us for more information focused on your needs. If you wish to receive information about RFID technology, subscribe to our magazine.






