RFID Serving Logistics
Radiofrequency technology has experienced exponential growth in recent years as companies have become aware of its benefits and potential.
What is RFID Technology?
Radio frequency identification is a technology that emerged in World War II and is increasingly present in everyday life. RFID is the automatic process of identifying objects by exchanging data through electromagnetic waves between two specified points:
- Transmitter or control unit.
- Product at item level, grouping or pallet to trace.
So, what is identification? Assigning codes to goods and linking that code to information associated with those goods. As the world of RFID is very extensive, in this article we are going to focus on passive RFID technology, which, unlike active, uses tags that do not have their own power source (battery). They have no energy autonomy and the RFID device is usually small in size. Its electrical current is activated when we bring a RFID reader close, which generates a response. There are various frequencies within the passive RFID world. The main ones are shown below:
- LF (Low Frequency): It operates in the 125 to 134Kzh band. Low frequency is suitable for applications that require reading small amounts of data and for short distances. It penetrates well into materials (water fabrics, wool), uses very small antennas through coils and is a very developed technology. On the other hand, it does not penetrate or transmit over metallic materials, filters small amounts of data, the reading speed is slow, the reading range is minimal and the identifiers are expensive. This frequency is usually used for animal identification.
- HF/NFC (high frequency/near field communication): operates in the 13.56Mhz band. Suitable for applications that require reading small amounts of data and for short distances. Penetrates well into tissues and water, simple and cost-effective antenna design, transfer rate higher than 134 KHz, small tag size. On the other hand, there are differences in powers allowed in different countries, does not penetrate metals, antennas and tags relatively large, reading range is short (up to approximately 10cms). Within this range is the NFC technology, increasingly developed and integrated with most mobile phones. Access cards usually use HF technology.
- UHF (ultra high frequency): operates in the 860 to 915Mhz band. Suitable for applications that require transmission distances greater than the previous bands, while maintaining a minimum tag cost. The tag size is relatively small, high data transfer, possibility of using directional antennas, reading distances of up to 8 meters. On the contrary, there are problems of signal absorption in aqueous environments and does not penetrate metals. It is the range on which we focus and the one of the labels manufactured by Trace ID.
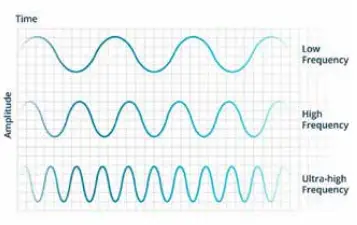
Source: Impinj. Wave amplitude and time with their respective frequencies.
How Does a Passive UHF RFID System Work?
At the device level, three elements are essential: the UHF RFID tag, the antenna, and the reader. The UHF tag is associated with a product, either hooked, sewn, nailed, etc. When this tag passes through the electromagnetic field of the antenna, it is activated and collects information from its chip. This information is bounced back to the antenna and the antenna transmits it to the reader. Then this “code” is processed to give a logical information that usually appears on screens/tablets. For all this to work, something essential is needed: a middleware software development to create that layer between logical data and have truly usable information/data. Without this layer, all the data received would not logically correspond to anything.
Differences between RFID and Barcode
What does passive UHF RFID technology offer that barcodes cannot? Although they are different, both technologies can be perfectly complementary.
- No human intervention is required as it can be automated.
- Readings are multiple and very fast.
- Each tag is identified individually.
- They have the ability to store information.
- They can be re-recorded countless times.
- They have a high degree of security.
- Real-time inventory (fixed points).
- Inventory in minutes (portable PDA).
- Automated / unassisted update.
- Elimination of human errors.
- Prevention of hidden inventory.
- Detection of stock deviations.
- Reduction of thefts.
- Process parameterization.
What does Trace ID do?
Since 2007, Trace ID has been the leading company in Spain for RFID label manufacturing. With its own production structure (unique in the country), it has the capacity to customize each product and offer tailored solutions. With state-of-the-art bonding (insertion of the chip into the antenna) and converting (conversion into a label according to customer requirements) from Muhlbauer, it can adapt to the demands of an ever-expanding market. It has its own R&D team capable of designing specific antennas for certain projects that require a certain complexity.
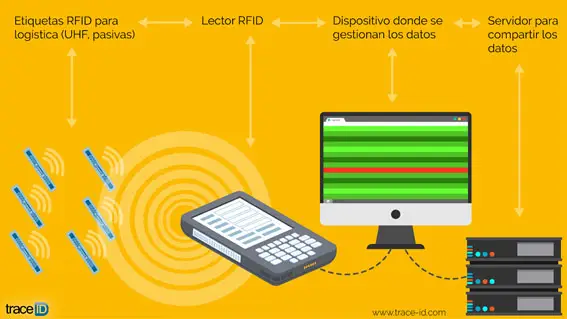
Source: Trace ID. Operation of a Passive UHF RFID System
RFID Technology in Logistics Processes
RFID solutions for logistics bring together a wide spectrum of usability. They can be found in almost every business process. For example, from tracking returnable transport units in the supply chain to managing retail inventories. The automatic control of logistics is one of the main challenges today and RFID technology is an essential tool for it.
Automatic management with RFID technology has the capacity to significantly improve global logistics chains. It also increases the overall efficiency of identification processes. Major retailers and their suppliers are already tagging pallets, boxes and other returnable transport units (UTRs) such as plastic boxes used for fresh food. On the other hand, logistics is also the control of retailers’ inventories. That is why logistics is so broad and complex. As we have said, the definition of logistics gathers many commercial processes. Below, you can find the main benefits of automatic logistics control with RFID technology.
• For manufacturers: better customer service, process optimization, faster billing, optimization of shipping documents.
• For distributors: more accurate shipping, faster and reliable deliveries, better traceability, greater cost savings
• For retailers: faster processes, less stock breaks, cost savings, better customer service, security.
In Spain, 52% of the RFID tags consumed are destined for RFID systems for logistics. The rest are applied in access control, machinery control and consumables in the health industry and also hospitality, in product security in retail stores, in sports timing and production processes, or in improving the customer experience, among others. In addition, RFID tags can meet various needs for traceability, security and marketing.
Logistics has not been immune to the digital transformation that has redefined our society in the last two decades, from people to organizations. In some way, the change has been generated as defensive and adaptive strategies to changes in consumer behavior, changes in international communications or changes in manufacturing processes. However, it has ended up revealing itself as a powerful generator of opportunities. Opportunities for greater efficiency and also for greater benefits, both implying greater competitiveness of the company. A key case as an example is ecommerce.
In the face of the immense increase in digital transactions, logistics has faced the challenge by becoming faster, more secure, more reliable, more flexible, and also more profitable. These changes have been made possible to a large extent by the adoption of new technologies and systems such as RFID, Block Chain, Big Data, CRM and ERP.
In the future, it will be rare if any company has not implemented RFID technology in any of its processes.

Carlos Martínez.
cmartinez@trace-id.com
Contact us for more information focused on your needs. If you wish to receive information about RFID technology, subscribe to our magazine.






